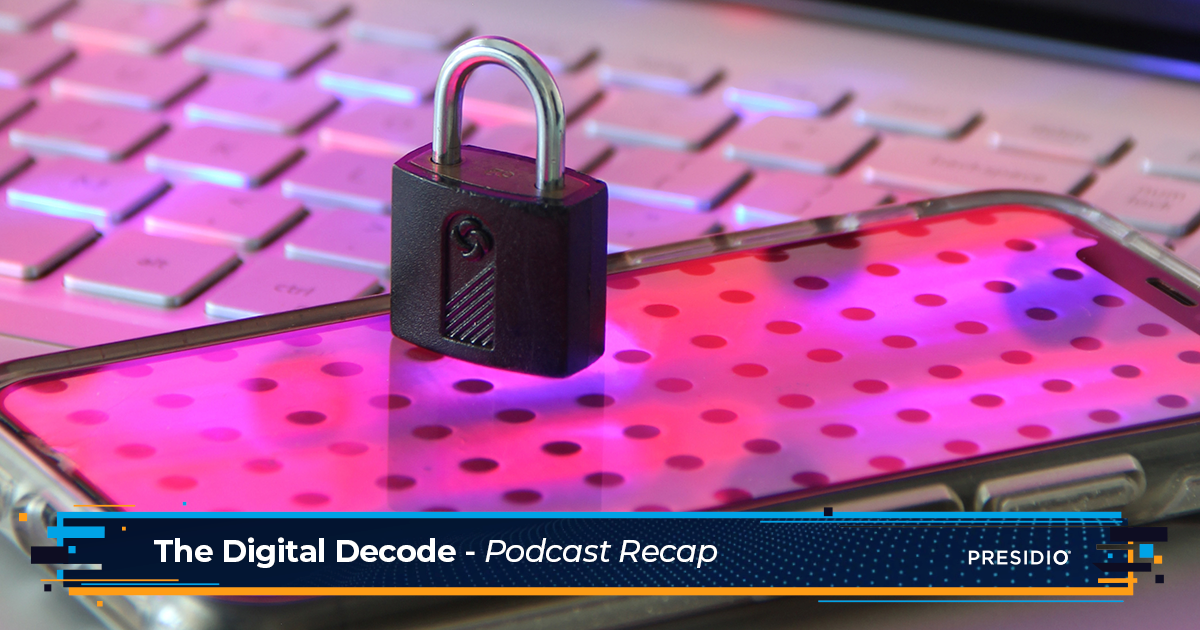
The world is evolving, and that includes the world of cybersecurity. The new national cybersecurity strategy emphasizes 5 pillars and their implementations. What does this mean for the public and Private sector? What is the role of AI in the current threat landscape?
Dan Lohrmann, Field Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) for Public Sector at Presidio, and Dave Trader, Field CISO at Presidio, discuss how partners are using AI to improve resiliency, automated backups, and detect fake reviews. What will the role of advanced intelligence and security be moving forward, and will the new national cybersecurity strategy released by the Biden administration be enough for consumers and citizens alike to remain safe.
The Ins-and-Outs of the Five Pillars of the National Cybersecurity Strategy
Three years into the Biden administration, a little later than most, the highly anticipated new national cybersecurity strategy has been released and there are quite a few unique takeaways to mention.
There are five ‘pillars’ put in place to unify global cybersecurity efforts and strategies so those working in cybersecurity are better aligned in their efforts and can come together as one line of defense.
The five pillars are as follows:
- Defend critical infrastructure
- Disrupt and dismantle threat actors
- Shape market forces to drive security and resilience
- Invest in a resilient future
- Forge international partnerships to pursue shared goals and implementations
The first pillar encourages cybersecurity teams to build technologies and develop policies and procedures to ensure critical infrastructure remains secure. This includes the systems holding society together such as financial institutions, transportation systems and emergency services.
The second aims to put an end to cybercriminal networks by investigating and acting accordingly. Each threat requires a different approach — you can’t put a fire out with a pair of handcuffs, but that doesn’t make it any less of a threat. Understanding each cybercriminal network, how they function and why is a necessary ingredient for long-term justice and resolution.
The third pillar incentivizes the development of secure technologies and practices, funding research and certification programs to encourage the adoption of said practices. The strongest technologies can’t address security issues if no one knows how to use them. These programs, research and practices are table stakes for proper implementation.
The fourth pillar prepares cybersecurity professionals for future threats by investing in new technologies, developing a skilled team and promoting education — working in-hand with the third pillar, professionals can address the present and future of cybersecurity.
Lastly, the fifth pillar recognizes that taking on cybersecurity threats is a global effort and therefore, it’s necessary to form international partnerships to combat any cyber crimes.
How the need for a hardened cyber insurance market will take center stage
The cyber insurance market is expected to take center stage as cyber-attacks become more frequent and businesses are increasingly dependent on technology for their work and storage of information.
However, before that happens, Dave believes some changes have to happen.
“The cyber insurance industry needs a little bit of maturity when it comes to what they’re insuring, who they’re insuring, and what it takes to protect that type of environment. Everyone’s still learning about this.”
One of the biggest challenges currently facing the cyber insurance market is ensuring the right controls are applied to the right industry. This requires more expertise on the part of the insurance providers and the businesses seeking coverage. Cyber insurance companies need to work on customizing their approaches to insurance as opposed to providing a one-size-fits-all solution.
Dave hopes to see cyber insurance become more of a requirement as it progresses in both quality and need.
Transforming the digital landscape to address cybersecurity concerns
Technology in the cybersecurity industry is always advancing and changing to keep up with new threats, devices and sites. With the captivating emergence of AI, specifically conversational applications anyone can interact with, new tools are constantly being pushed by industry leaders and tech startups alike.
Software like the cloud provides more advanced security measures and expertise than most organizations can implement on their own. Since cyber threats are becoming more frequent and complex, keeping up to date with security measures is important to ensure a safer cyberspace.
It’s never a bad thing to reach out for help and partnership when you aren’t equipped to address your security concerns. Where there’s a threat, there’s an expert ready to help
In a digital world of never-ending tools development, reducing the number of tools and providing more protection for less money is a top concern, storming cyber conversations everywhere. Legacy systems are at the center of this debate as they are outdated software that oftentimes lacks the necessary security measures to properly protect from threats.
It’s important to modernize legacy systems and all other cybersecurity technology, possibly migrating them to the cloud whenever possible to reduce the risk of data breaches.
“The challenges are going to continue over the next six to 12 months,” Dan says. “Keeping up, quite frankly, is a moving target.”
Want to learn more about the five pillars of the national cybersecurity strategy, what to expect from the cyber insurance industry and why it’s important to keep up with the latest cybersecurity tech? Listen on Apple Music, Spotify or wherever you find your podcasts.